Everything about the Strawberry Tree and Medronho!
The fruit, the plant, the tree, development conditions, profitability, investment, non-refundable subsidies, community funds and the potential of this species rooted in Portugal. A 360º look at the future of strawberry trees and their potential for appreciation in the context of orchards, agroforestry and other options.
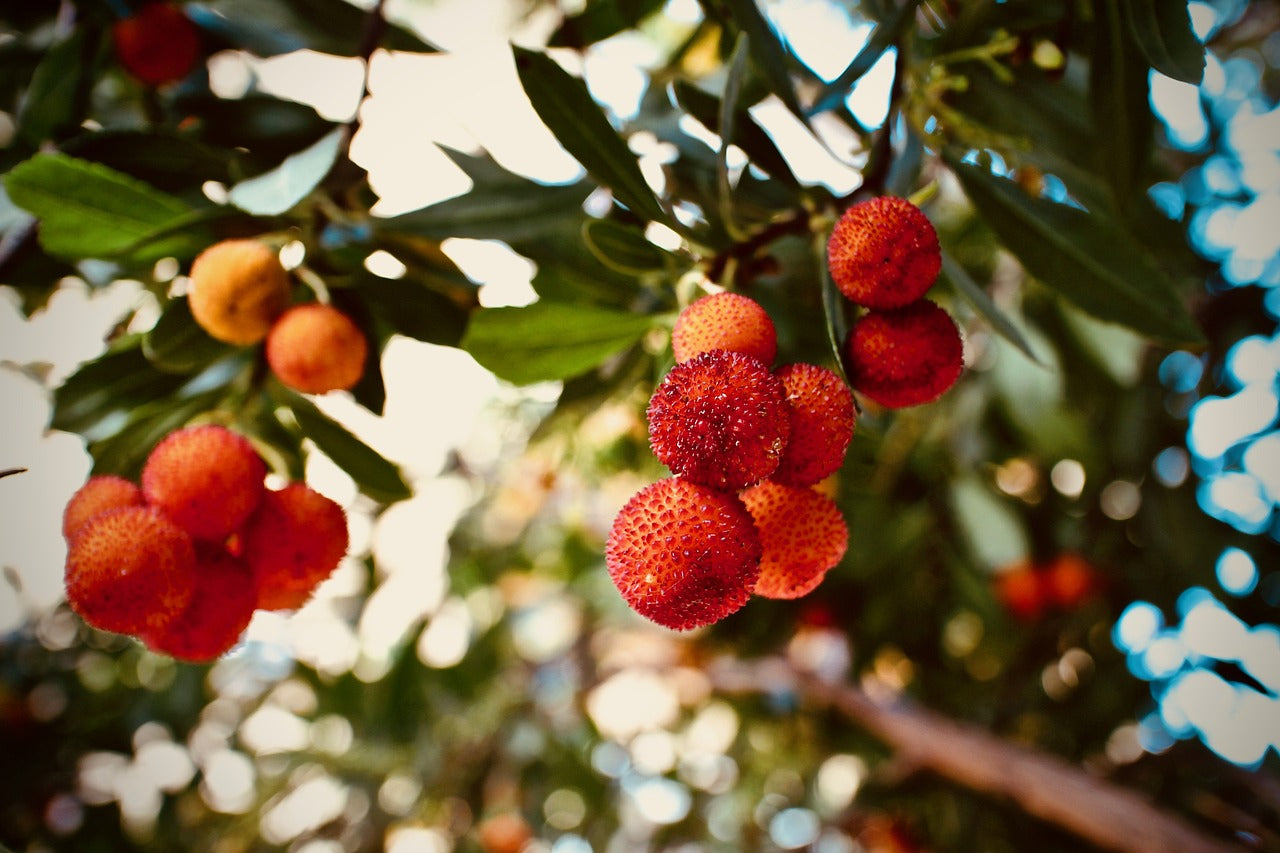

Medronho , the species and origins,
Scientific name : Arbustus unedo
Common name : Strawberry tree
Family : Ericaceae
Genus : Arbutus
Origin : The strawberry tree ( Arbutus unedo ) is an evergreen tree native to the Mediterranean basin, known for its highly nutritious fruit.
In Portugal, it is cultivated especially in Baixo Alentejo and Serra Algarvia, being used both for fresh consumption and for the production of brandy.

Best known for the fruit....
The arbutus is a red fruit and belongs to the category of “small fruits ”, being a round and warty berry, of an intense red color when ripe.
Before reaching its intense red state, it goes through various stages of green, yellow and orange coloration. The best-known component of the strawberry tree is its fruit.
Can you eat the arbutus? The arbutus is an edible fruit , used in cooking, baking and other areas for its recognized antioxidant, astringent, anti-inflammatory, antiseptic, depurative and diuretic properties.

From the medronho tradition to new ways of tasting it. What is the medronho used for?
Despite all the potential uses, the oldest and most popular use continues to be Medronho Brandy.
Medronho brandy is a spirituous, aromatic and colourless drink. Its versatility allows it to be added to various cocktails or simply drunk with coffee, a common practice throughout the country and especially in the lower Alentejo and Algarve where the drink is best known and appreciated.
Other applications :
- fresh food and culinary applications for its antioxidant properties, sugar level (sweets, jelly, jam, yogurts, cakes, chocolates, bread, vinegar, gelatin...)
- Arbutus honey is a very specific honey due to its bitter taste, reminiscent of coffee. It crystallizes quickly and has a dark brown color.
- alcoholic liqueurs . gin, vodka and medronho beer are already available on the market
- Use of its leaves for infusions . Its diuretic and antiseptic properties can be used for homeopathic purposes.
- Its leaves and bark are also used for tanning leather, as they are rich in tannins.
- strawberry tree branch for ornamental purposes
- The wood from this bush, in addition to being good quality firewood, is also used to make charcoal.
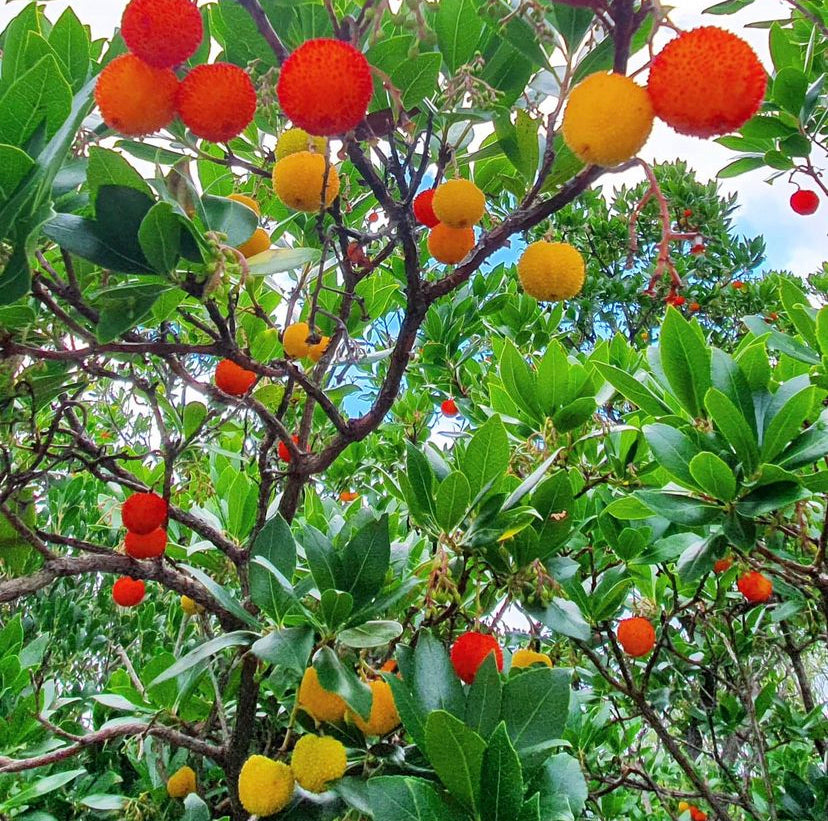

The Strawberry Tree with Christmas decoration
Between November and December, the strawberry tree has colors that remind us of a Christmas tree: green, yellow, orange and red fruits and white and pink flowers.
Strawberry trees grow favorably and spontaneously in poor, schist soils , especially in the regions of Alentejo, Algarve and the interior of the Central and Northern Regions of Portugal.
The strawberry tree normally grows like a shrub up to a height of approximately 5 meters with erect branches that sprout from the trunk 0.50 meters above the ground and are also quite spaced apart.
The strawberry tree's crown is rounded with persistent, elliptical leaves that take on a dark green color similar to that of the cork oak, and also have a waxy shine on the upper surface.
The flowers of this strawberry tree are white or slightly pink in color and are very decorative . If you want to know more about the exploitation of the tree , contact us !
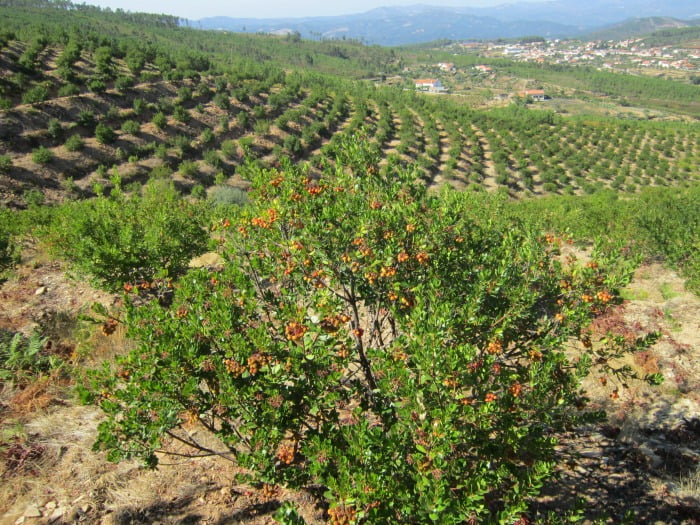

Looking at the future of strawberry trees and the medronho,
The best agricultural and forestry practices are now also being used in the exploitation of this species.
Knowledge of other fruit trees reached Medronheiro, allowing for a higher quality final product for the consumer.
Some practices such as : the arrangement of strawberry trees in orchards, the choice and selection of trees with the best fruits, watering, pruning operations, pruning, among others, allow a higher quality product to consumers.
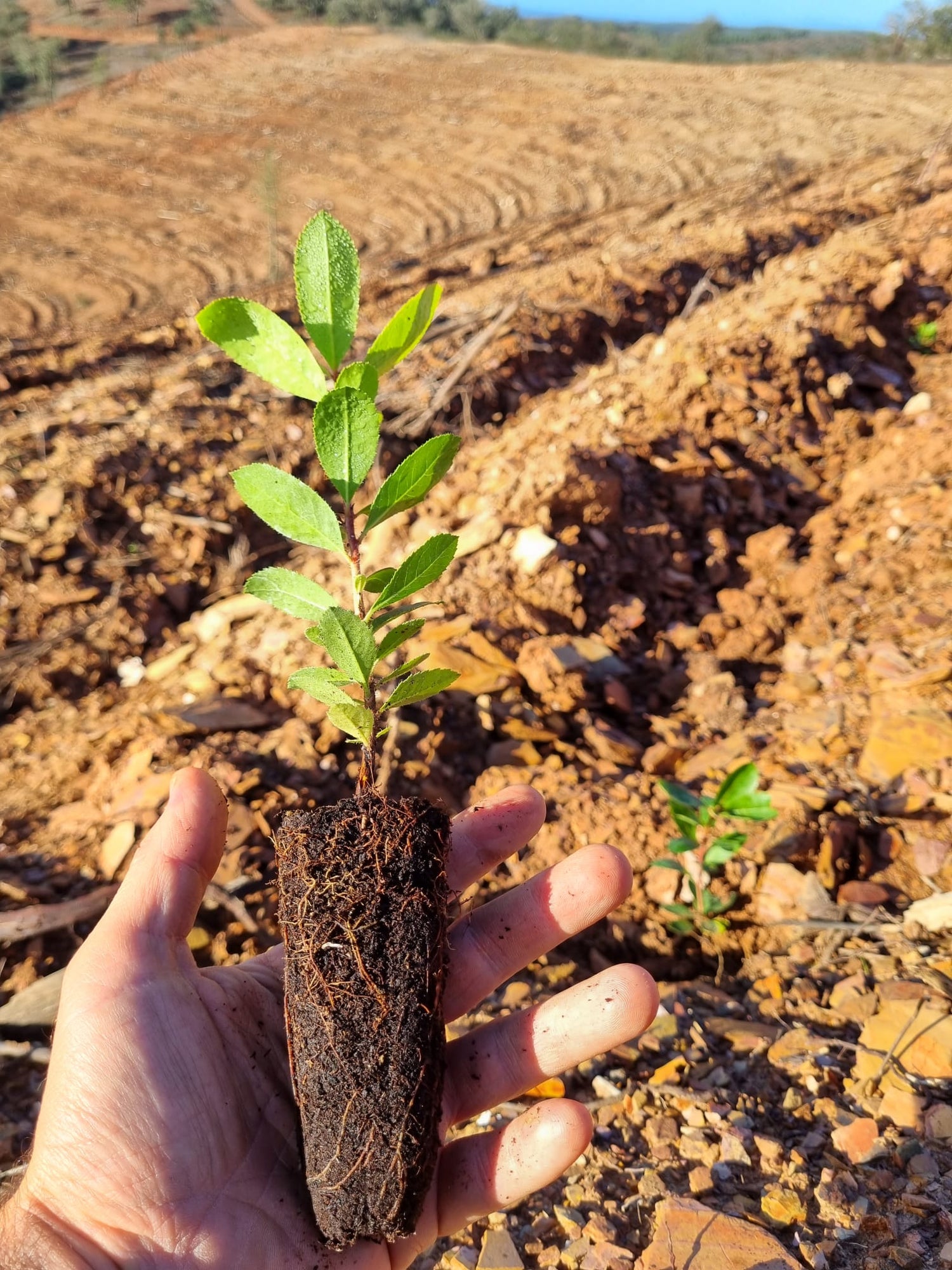

How to plant or sow the strawberry tree?
The most common practice is to plant the strawberry tree in the ground when it is already around 15 to 50 cm tall and with a developed root system .
Techniques such as sowing seeds directly into the soil or propagation by cuttings have a very low success rate.
In the lower Alentejo, under dry conditions, the common practice is to plant at the end of winter .
The time of year to plant strawberry trees will depend on several factors such as the climate of the area, soil quality and whether or not you have access to water to irrigate the strawberry trees.
Highly recommended for areas with high exposure to frost, the placement of micro-perforated protective tubes. If you want to know more about planting, contact us .
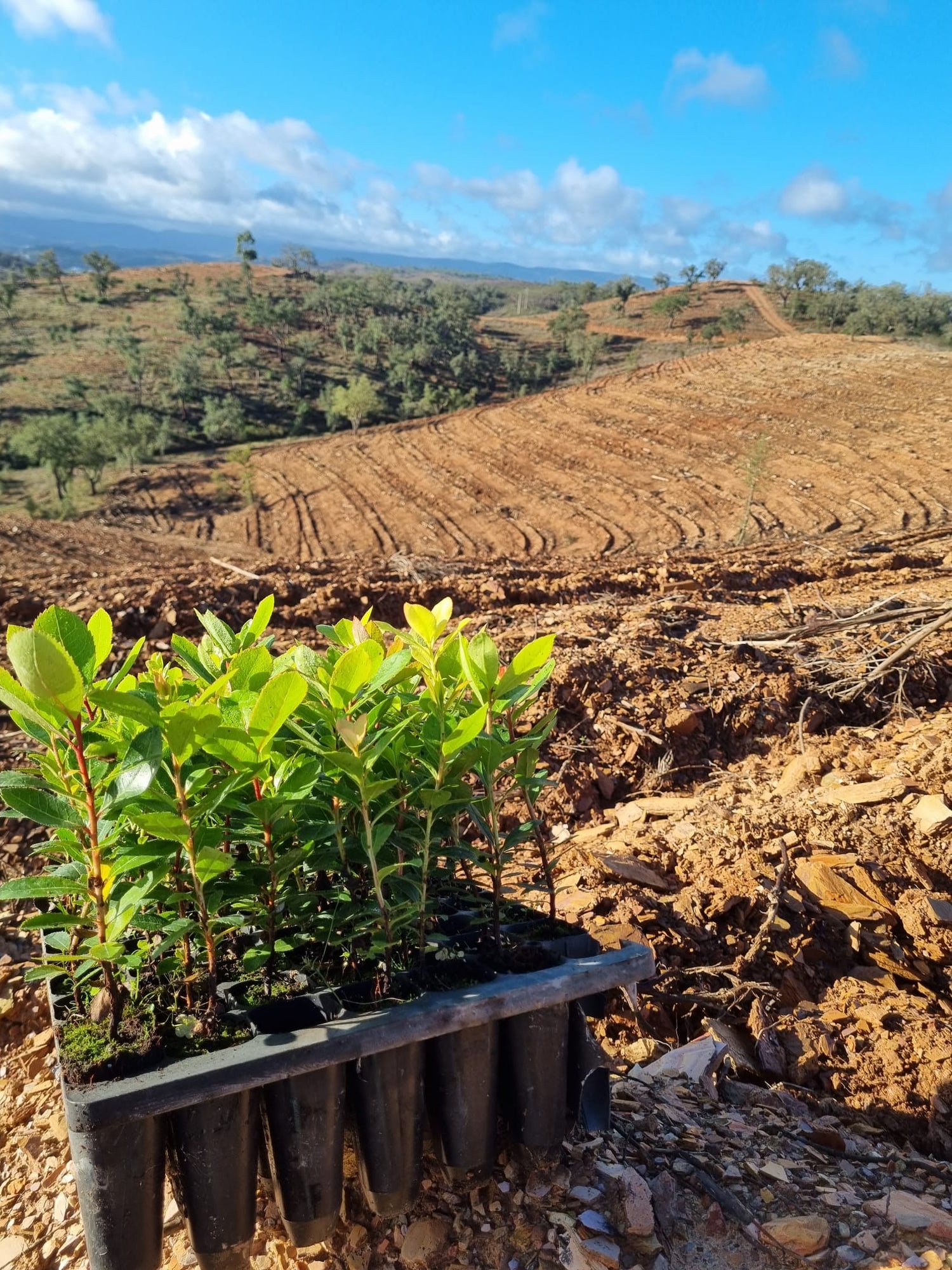

How should the land be prepared to plant strawberry trees?
Each location is unique, but some factors are critical for good site preparation such as:
- Soil analysis (measuring the richness of the soil in terms of macro and micronutrients, organic matter and pH levels are the minimum that should be assessed). Based on these, it will be possible to assess whether there is a need for any treatment or correction of the soil necessary for the correct development of the plant after planting.
- Land mechanization , with a view to developing the strawberry tree, you should take some actions such as:
- Deforestation (cleaning, removing existing vegetation, reducing competition with plants and increasing their exposure to sunlight) with incorporation of plant matter into the land.
- Soil corrections such as organic matter, pH correction or others necessary taking into account soil analysis.
- Ripping the soil , ripping allows, when the ripper is used on dry soil, to fracture the compacted horizons, thus increasing the volume of available soil. This operation is extremely important, as it will facilitate the penetration of roots into the soil, while at the same time facilitating drainage and water infiltration.
- Ridges , in some areas ridges may be created for planting the tree.
The operations can be more or less complex depending on the location and its condition . If you want to know more about preparing land for the installation of strawberry trees , contact us.
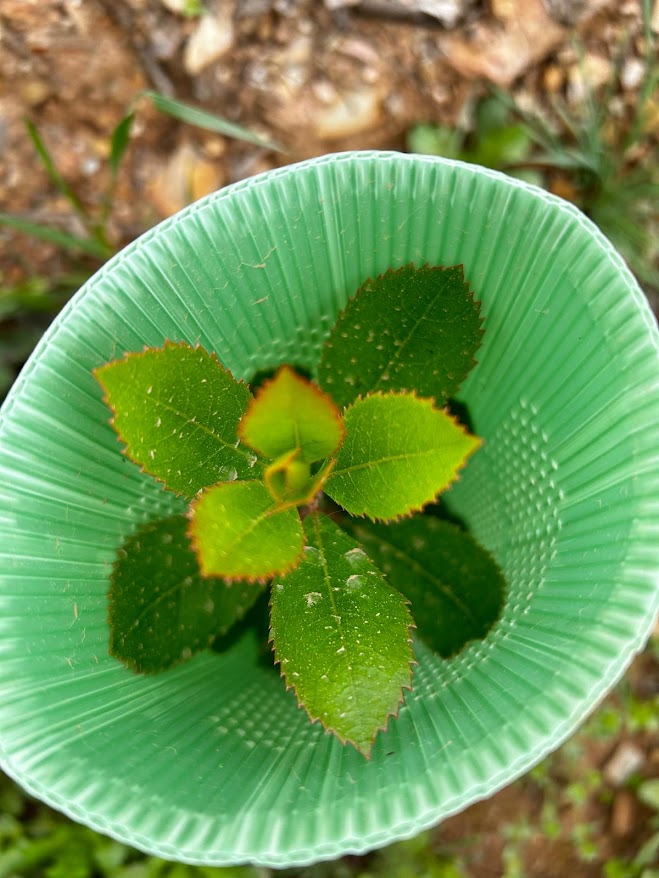

What are micro protective tubes for in planting?
Micro-protective tubes, despite being yet another investment in planting, have numerous benefits, including:
- Ensures efficient and correct growth of the aerial and root parts
- It retains moisture directly to the root zone. It produces a microclimate that is favorable to the survival and growth of the plant. It protects from direct sunlight.
- Protects the plant from rodents and larger animals, strong winds and frost
- Reusable and/or Recyclable
An investment to consider not only for the reduction in mortality rates but also for bringing forward the plant's entry into production.
Note : buy tubes suitable for strawberry trees (micro-perforated, with a border at the top, 40 to 50 cm)
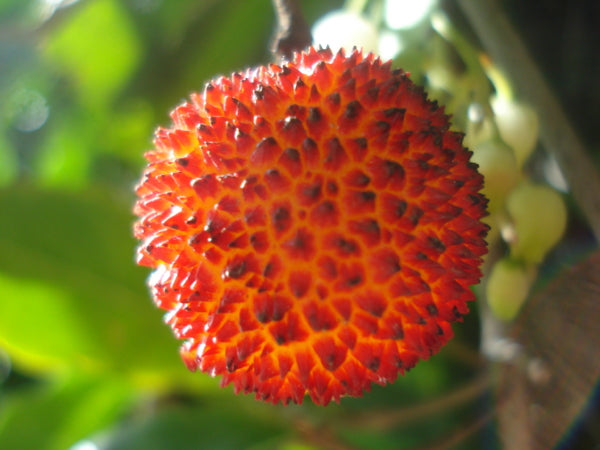

How long does it take for the strawberry tree to bear fruit?
The search for profitability with the Medronho fruit makes this one of the most recurring questions.
Strawberry trees grown under dry conditions in the lower Alentejo come into production between 3 and 5 years , with the most common period being the 4th year.
This time can be reduced depending on some factors such as: choice of plants, land preparation, quality of the plantation, irrigation systems, among others.
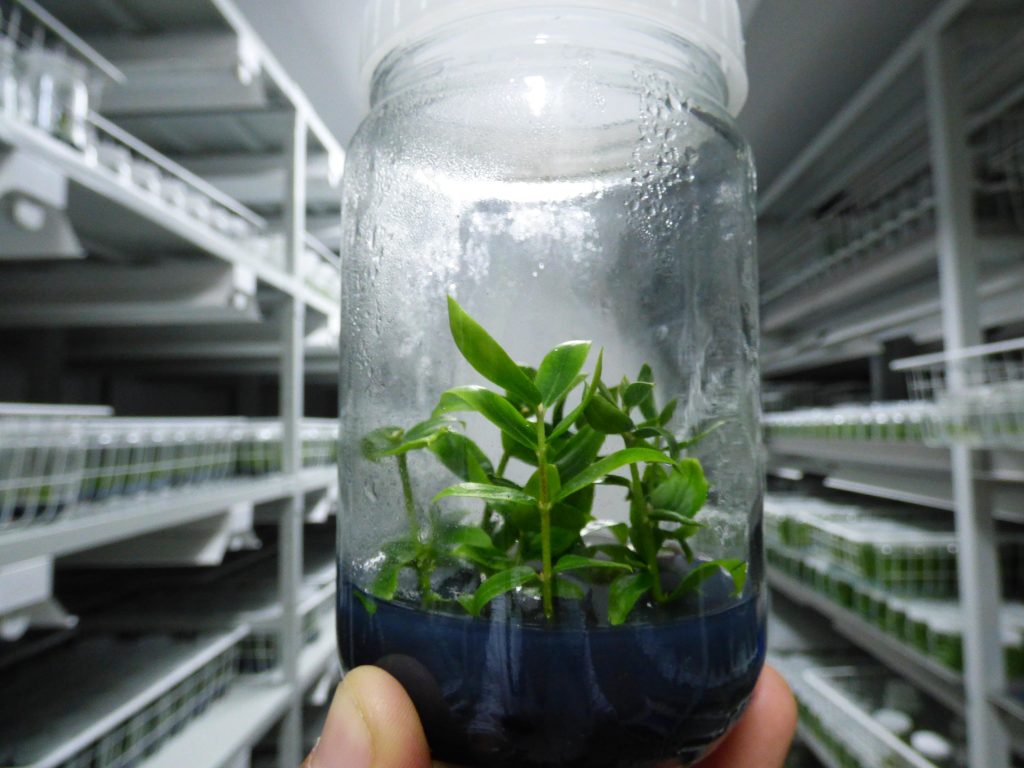

What is the difference between cloned strawberry trees and those of seminal origin?
Cloned strawberry trees are a replica of the tree from which they originated, thus having characteristics exactly the same as the original.
Strawberry trees of seed origin are collected from the seed of a fruit taken from the mother tree. In a simplistic way, these seeds do not guarantee that they are the same as that "mother" tree (as they are influenced by the mother tree and the father tree).
Cloned strawberry trees are obtained through micropropagation or cuttings techniques, and their value is 4 to 10 times higher than that of a strawberry tree of seed origin.
Should I opt for colonized strawberry trees?
There are several topics to address when selecting plants and their origin. To find out more, do not hesitate to ask for more information.
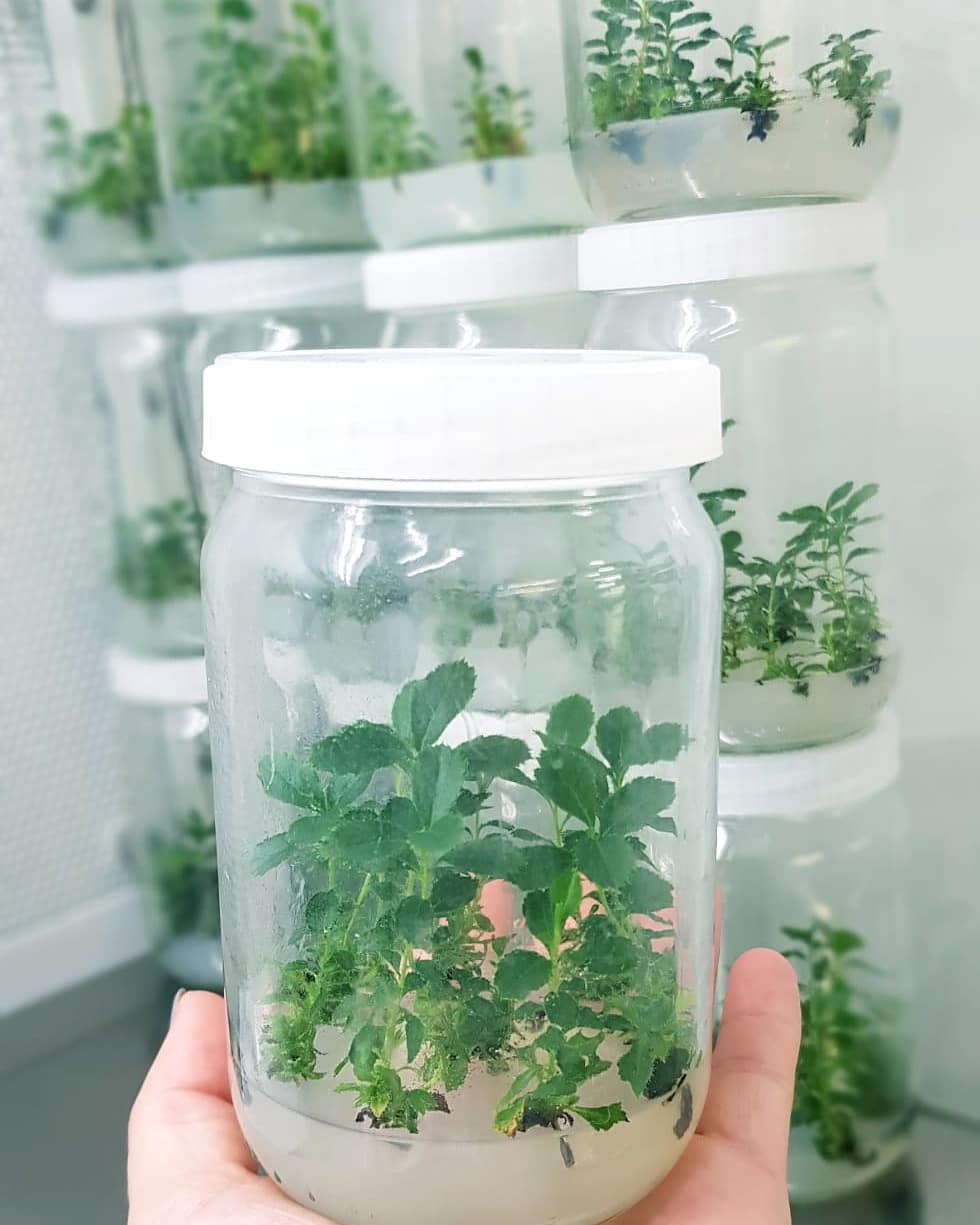

Should I choose colonized or seminal arbutus trees?
At the end of the day, it should always be a choice based on the goals you have for the plants or orchard.
If you want to maximize fruit production, colonized strawberry trees are undoubtedly the choice (a higher investment).
However, you should bear in mind:
- What is the origin of the clones?
- ensure genetic diversity in your orchard, to reduce exposure to potential pests and diseases
- There are good orchards of seed origin with much lower investments (correct choice of nurseries)
Where should I buy strawberry trees? Associated with your choice of the origin of the plant is where to buy it. Given the variety of supply available, take into account several factors other than price, especially:
- ICNF certified nurseries
- origin of the seed or clone. Have a phytosanitary passport - DGAV
- ask for references and visit orchards that your potential supplier has used
To find out more about productivity and tests carried out with several plants , contact us.
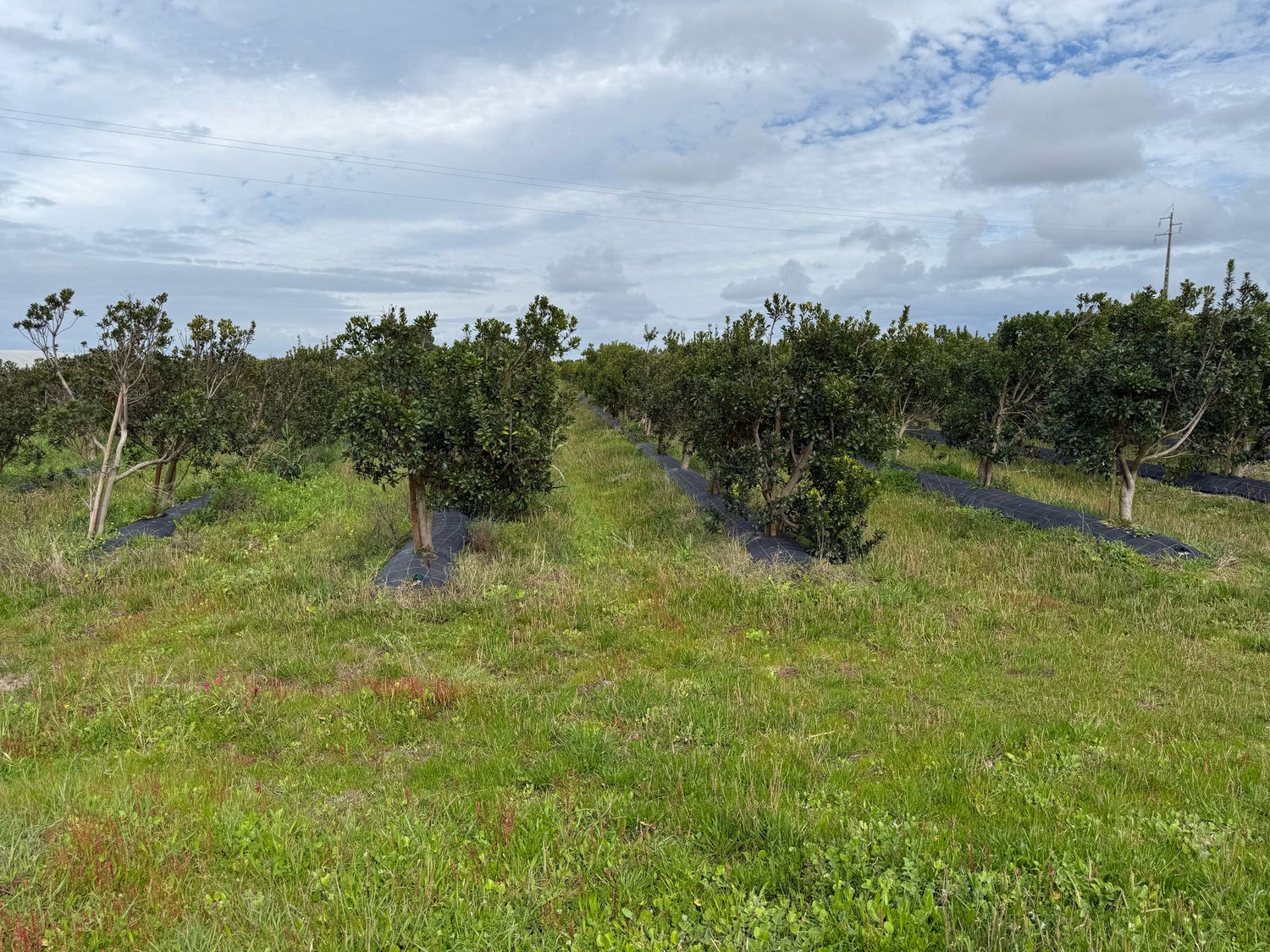

How many strawberry trees should I put per hectare?
Strawberry tree orchards should have between 400 and 1000 plants per ha .
The three main factors in defining the number of strawberry trees to plant per ha are:
- definition of what purpose we want from plants (branches, fruit, forest and association with other species)
- slope and inclination of the land where the orchard is installed
- How the orchard will be managed in terms of pruning and formation of strawberry trees

How many kilograms (kg) does a strawberry tree produce per tree?
Production per tree varies greatly depending on age, plant type (seedling or clonal), soil, and the presence of irrigation, but there are average values that can help provide guidance.
- Young plants (4-5 years): 1 to 3 kg/plant
- Start of full production (6–8 years): 3 to 5 kg/plant
- Adult plants in good condition: 6 to 8 kg/plant
- Clonal plants under irrigation (ideal scenario): can exceed 8 kg/plant
In poor or unirrigated soils, production is naturally lower. However, in areas with good moisture or with drip irrigation support, productivity per plant increases very significantly.

How much does it cost to plant one hectare of strawberry trees?
Knowing the installation cost is an essential question for anyone considering investing in strawberry tree cultivation — but the answer varies considerably. The cost can range from R$ 2,500 to R$ 12,500 per hectare, depending on several factors:
- Current terrain conditions (slope, undergrowth, access)
- Soil type and need for preparation operations
- Need for initial soil corrections and fertilization.
- Type of plants chosen (origin, size, certification)
- Use of personal protective equipment, braces , and other support materials.
- Chosen system : dryland farming or irrigation system with fertigation.
Each project needs a customized budget. We can help you create that estimate based on your land.
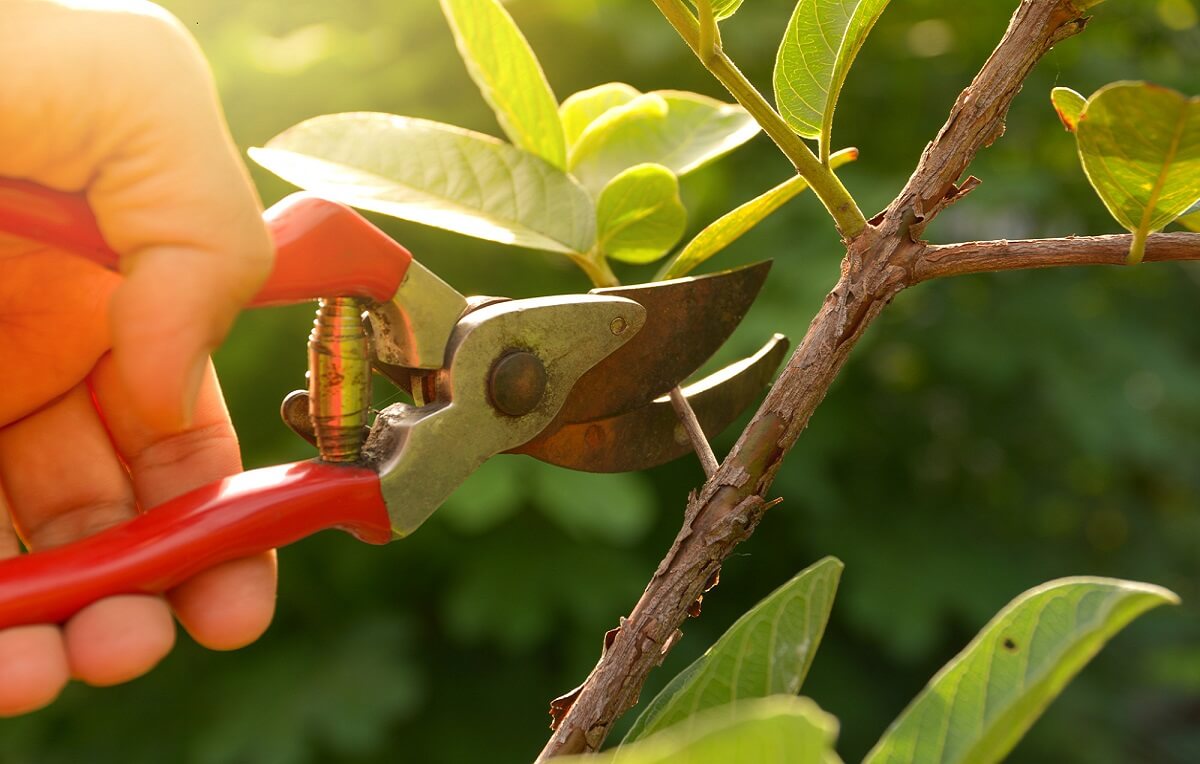

When and how should I prune strawberry trees?
Strawberry trees should always be pruned during their dormant period .
In most situations, the strawberry tree grows in shrub form, without any intervention that would allow for the renewal of new branches. Most pruning interventions are aimed at reducing the size of the shrub and facilitating harvesting .
Training and shaping pruning are critical for those seeking to increase fruit production per tree. When "choosing" the tree's shape, you can opt for a "vase" shape, a "covered central axis" shape, or others.
Pruning, branch removal, or topping, which are more aggressive interventions, may be necessary for large trees, trees in areas burned by fire, or other conditions.
How do you prune strawberry trees?
The basic principles of pruning operations are aligned with the pruning of other fruit trees and are based on widely tested and disseminated knowledge. The main question to be answered is what shape you want to give your trees, how you want the pruning to be conducted.
Contact us To learn more about pruning strawberry trees.
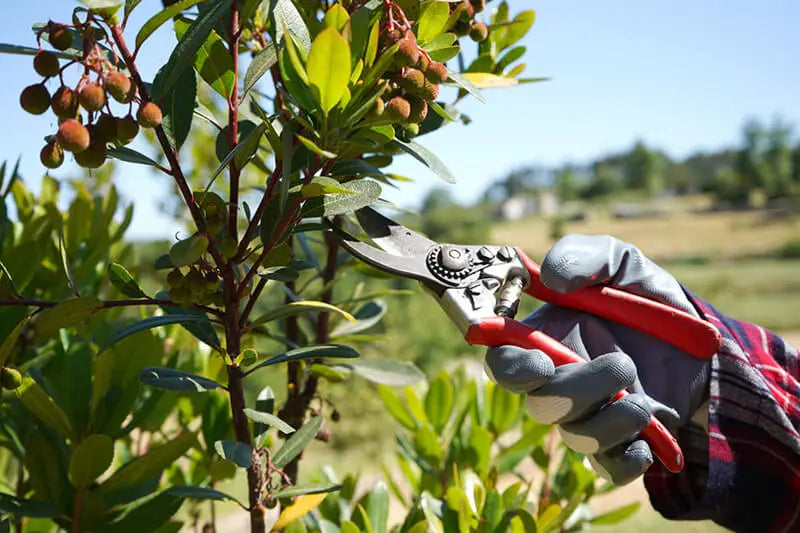

What characteristics determine the pruning of the strawberry tree?
The general principles of pruning are common to several fruit trees, but the strawberry tree has some specific characteristics such as:
- Evergreen shrub or small tree. Under good growing conditions it can reach several meters in height.
- Without significant apical dominance
- Older wood contains dormant buds that, after stress (intense pruning or destruction of part of the wood burned by fire), sprout and produce new shoots.
- Great capacity to regenerate from torga. The thicker roots contain reserves and dormant buds.
- The flower clusters originate from terminal buds that are ready (they form in the same year they develop), meaning they always bear fruit on new branches.
- From flowering to harvest, 10 to 12 months elapse; and it is common for the harvest season to coincide with the flowering of the tree that will produce fruit the following year.
- Maturation and flowering usually occur between October and December; there are also plants that, under certain conditions, have ripe fruit in August.
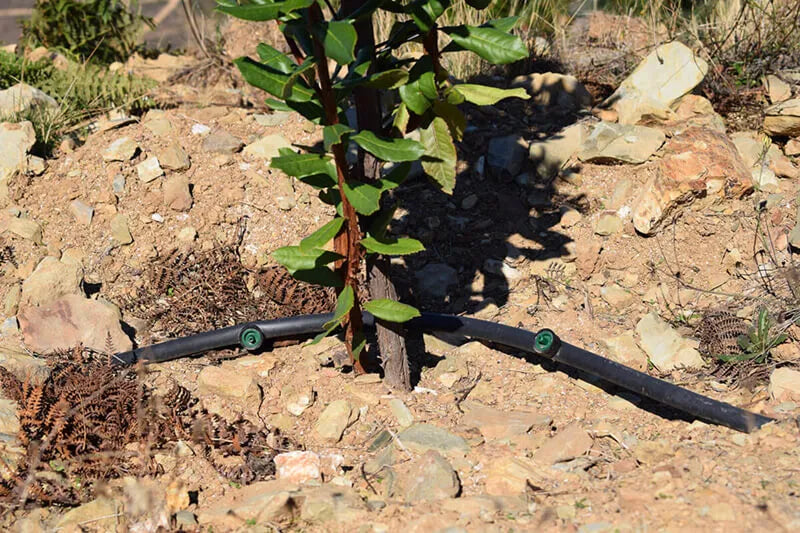

Should I water the strawberry trees? Can I use fertigation?
The strawberry tree, like any tree, prefers optimal water conditions for its growth.
In most of the country (Portugal), established orchards do not have irrigation systems due to two reasons:
- high investments in irrigation systems
- difficulty accessing water
In mainland Portugal, the strawberry tree benefits from irrigation because the hot months of May-August are too harsh and cause water stress for the plants, jeopardizing the development of the plant and the fruit.
The irrigation plan should take into account the age of the plant, its phenological cycle, and the local moisture and rainfall conditions.
Fertilization via irrigation will be important if the plant has any nutritional needs, to control pests, or for other reasons. Note that this should also take into account the phenological cycle and soil analyses.
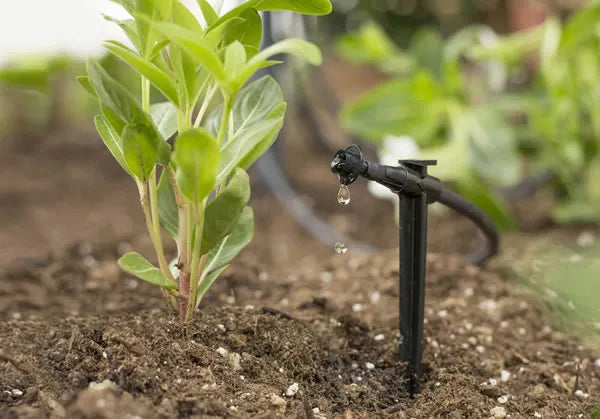

How much water do strawberry trees need?
A very common question and a simplistic attempt to find out more is "how many liters of water should I put in the strawberry trees?"
The answer is simple but not linear; it depends on each case and requires analysis of 5 factors:
- soil and climate conditions
- the phenological state
- the age and leaf and root development of strawberry trees
- The strawberry tree can withstand water stress, so it's necessary to understand the objectives of irrigation (plant survival, type of fruit).
- irrigation system installed
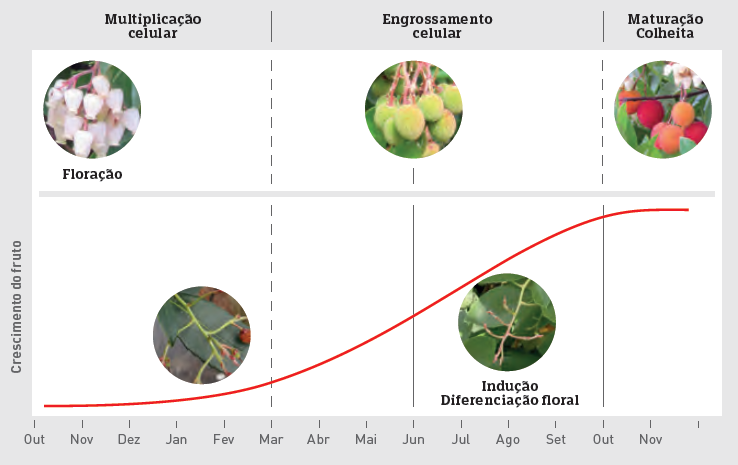
When do strawberry trees bloom?
Floral induction and differentiation occur between June and September.
From October to January, its small white flowers bloom in hanging clusters, while at the same time the ripe fruits from the previous year's flowers are ready to be harvested.
The strawberry tree at this time of year is one of the most striking species in our forest areas due to the variety of colors it displays (white, pink, green, yellow, orange, and red).

What are the most common disease pests in strawberry trees?
Strawberry trees are a hardy species that has only recently begun to be planted in orchards, always exhibiting great genetic diversity.
As such , there are not yet many pests and diseases affecting this crop.
The most common pests are: aphids (such as green aphids and black aphids), strawberry tree butterfly or "strawberry tree caterpillar," and strawberry tree moth; there are also several fungi, such as the one that causes the so-called black spot.
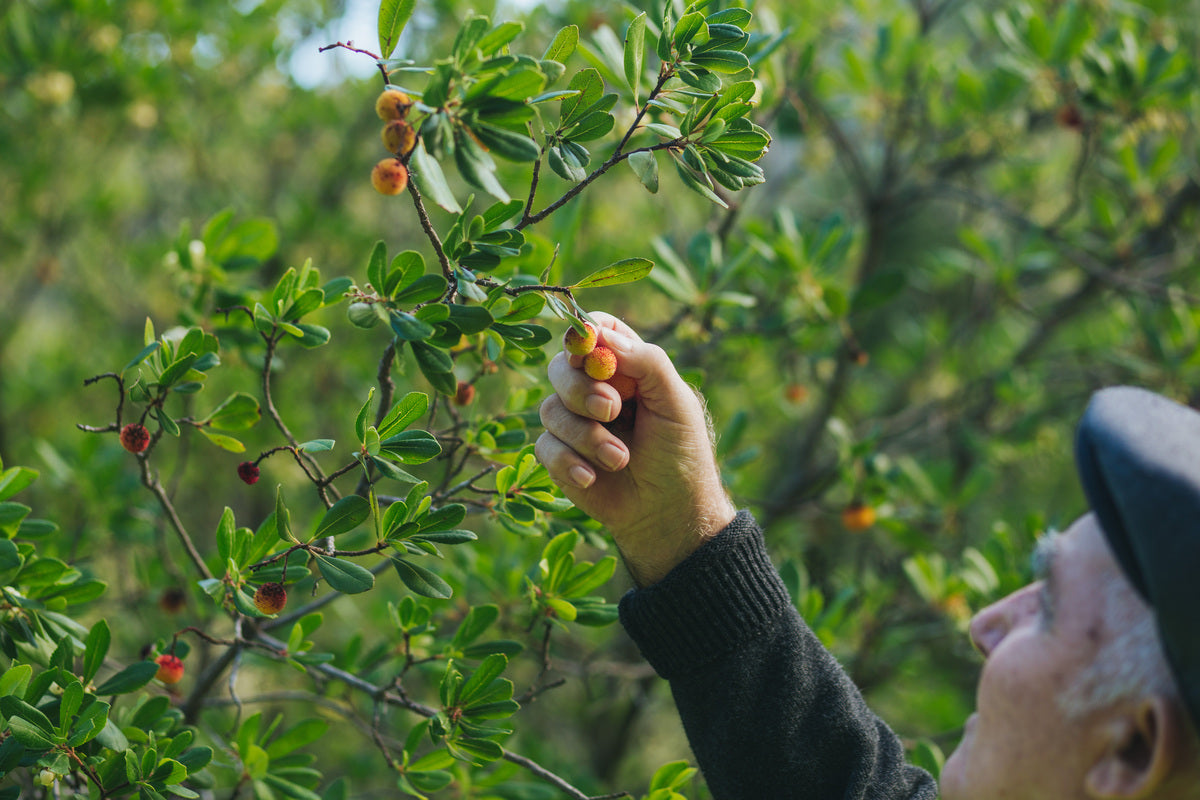

When does the strawberry tree fruit harvest begin?
The strawberry tree fruit harvest season begins in October and can last until January. Between November and December 15th is usually, in the lower Alentejo region, the time when 90% of the quality strawberry tree fruit is harvested.
This is a manual process of extreme importance for the quality of the famous Medronho Brandy . Only ripe fruits should be chosen; they cannot be "pecked" by birds or fermenting. Leaves and stems cannot be picked. All these factors contribute to the chemical and sensory quality of Medronho Brandy.
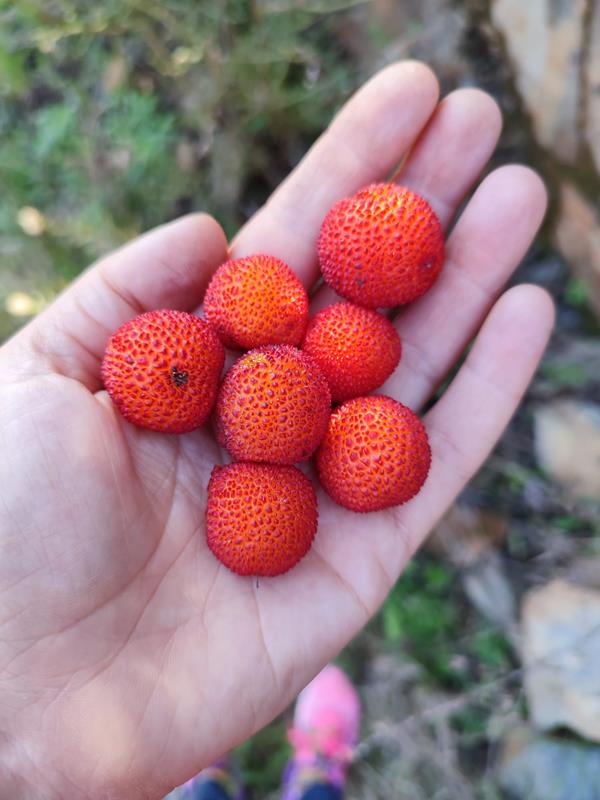

How much does 1 kg of arbutus berries cost?
Strawberry tree fruit for fresh consumption costs €6 to €12/kg . The market for fresh strawberry tree fruit is small in the national market.
The arbutus berries harvested to produce arbutus brandy cost between €1.5 and €3/kg , depending on the product's origin, Brix level, and harvest quality.
If you wish to buy or sell arbutus berries, please contact us.

Is strawberry tree cultivation profitable?
Many farmers and foresters wonder about the financial sustainability of their orchards.
Questions like "Does strawberry tree farming make money?" or "How much can I earn per hectare?" are frequent. The answer isn't universal, as it depends on several factors. However, there are critical points that influence profitability and deserve attention.
Profitability depends on several factors:
- Choosing the right variety and planting density.
- Irrigation system, soil quality, and marketing model.
- Poma investments and maintenance
- Financing is crucial : Support programs and community funds ( Young Farmer Project and others) can make the investment more viable.
With proper planning and good management , the strawberry tree can be a productive crop with a growing market.

How can I obtain subsidies for planting strawberry trees?
Access to community funds ( Young Farmer Project) and others) and national support can be crucial for the project's viability, but it requires a well-structured process.
There is community and national support for agriculture, but the process can be bureaucratic.
Common requirements:
- Minimum area required
- Initial investment and maintenance commitments
- A sound technical and financial plan to make the candidacy viable.
The Process: feasibility analysis → application → evaluation → project execution.
Having an experienced partner increases the chances of successful loan approval.

Is it possible to establish a strawberry tree orchard without significant investment?
The question is very simple and common among farmers in the lower Alentejo region and areas with poorer agricultural or forest soils.
Many farmers seek to reduce initial costs without compromising productivity... is this possible?
- Yes, but it requires efficient management of costs and available support.
- Strategies for reducing costs:
- Choosing the most suitable land.
- Optimizing planting density.
- Phased implementation of the project
- Apply for community funding as part of the Young Farmer Project or other programs.
- The balance between initial investment and expected return is fundamental.
- Leveraging community funds can minimize costs and accelerate profitability.
